Marshall Space Flight Center
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
|
|
Glossary
Atmosphere- The atmosphere of the Earth may be divided into several distinct layers, as the following figure indicates.
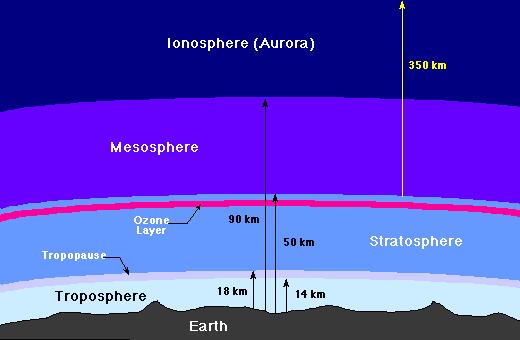
Layers of the Earth's atmosphere
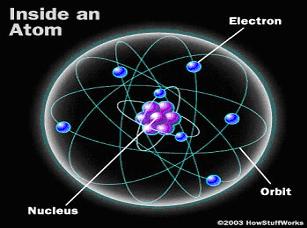
Atom- the smallest part of an element composed of three subatomic particles- protons and neutrons, which make up the nucleus, and electrons that orbit the nucleus.
Aurorae- appear during geomagnetic storms--that is, when Earth's magnetic field is vibrating in response to a solar wind gust
Dispersion-
Electron- the tiny subatomic particles which move in clouds at different energy levels around the outside of the atom. They have a negative charge.
Electromagnetic waves- oscillating electric and magnetic fields traveling together through space at a speed of nearly 186,000 mi/300,000 km per second.
Electromagnetic spectrum- The entire range of radiant energies or wave frequencies from the longest to the shortest wavelengths--the categorization of solar radiation. Satellite sensors collect this energy, but what the detectors capture is only a small portion of the entire electromagnetic spectrum. The spectrum usually is divided into seven sections: radio, microwave, infrared, visible, ultraviolet, x-ray, and gamma-ray radiation.
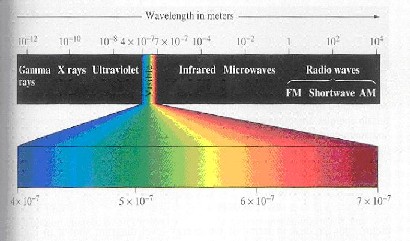
Click image to view larger version.
|
|

